|
|
 Navegación por listas
Navegación por listas
|
| Página de inicio | TAH partonomy |
| Nivel superior |
sistema cardiovascular  Corto Todo Corto Todo
|
| Nivel 2 |
corazón  Corto Todo Corto Todo
|
| Nivel actual |
pericardio 
|
| Idioma subsidiaria con latín |
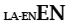 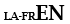 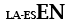
|
| Idioma principal no latín |
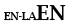  
|
 Lista partonómica
Lista partonómica
|
 Notas cientificas
Notas cientificas
|
| UID |
Libelle of note
|
| 3718 |
Membrana bronchopericardiaca A connective tissue membrane consisting mainly of collagenous fibres that extends from the anterior surface of the tracheal bifurcation via the dorsal wall of the pericardium to the diaphragm. Three fibre directions can be discerned. Vertical fibres run in the direction just mentioned. Transverse fibres run from the pericardium into the lung where they join the adventitia of the large pulmonary veins. Oblique fibres extend from the two main bronchi diagonally over the pericardium into the opposite pulmonal ligaments. The membrane is the borderline between the middle and the posterior mediastinum, together with the tracheal bifurcation. Its function is to stabilize the tracheal bifurcation and that of the main bronchi, in relation to the dorsal aspect of the pericardium and the pulmonary hilus, during movements relating to respiration, the larynx, and the head. Benninghoff Anatomie. 1994. Edited by Drenckhahn D. and Zenker W. Vol. 1. p. 557. München-Wien-Baltimore: Urban & Schwarzenberg. Rauber/Kopsch. 1987. Anatomie des Menschen. Edited by Leonhardt H. Vol. 2, p. 159. “Innere Organe." Stuttgart, New York: Georg Thieme.
|
 Firma
Firma
|
| Type of list | P3 |
| List Unit Identifier | 3715 |
| Subtotals | subchildren 0 subunits 0 |
| Proper children | 11 |
| Number of children | 11 (validated) |
| Proper units | 12 |
| Number of units | 12 (validated) |
| Signature | 314 (validated since 11.1.2025) |
| Fecha: 18.05.2025 |


